The Defects or Imperfections in the solids
Any deviation from perfectly ordered arrangement constitutes the defect or the imperfection. These defects sometimes are termed as thermodynamic defects because the number of these defects depends on temperature.
(1) The Electronic imperfections: Usually, electrons are present in the fully occupied lowest energy states. But at the high temperatures, some of the electrons might occupy higher energy state depending upon the temperature. For instance, in the crystals of the pure Si or Ge some electrons are released thermally from covalent bonds at the temperature above 0 K. these electrons are free to move in crystal and are responsible for the electrical conductivity. This type of conduction is termed as intrinsic conduction. Electron deficient bond formed by the release of the electron is called as a hole. In presence of the electric field the positive holes move in the direction opposite to that of the electrons and conduct electricity. The electrons and holes in the solids give rise to the electronic imperfections.
(2) Atomic imperfections/point defects: When the deviations exist from the regular or the periodic arrangement around the atom or a group of atoms in the crystalline substance, the defects are termed as point defects. Point defect in the crystal might be classified into the following three basic types.
(i) The Stoichiometric defects: The compounds in which the number of positive and negative ions is exactly in the ratios indicated by their chemical formulae are called stoichiometric compounds. The defects do not disturb the stoichiometry (the ratio of numbers of positive and negative ions) are called stoichiometric defects. These are of following types,
(a) The Interstitial defect: This defect is caused due to the presence of ions in normally vacant interstitial sites in the crystals.
(b) Schottky defect: This defect is caused the when equal number of cations and the anions are missing from their lattice sites so that electrical neutrality is maintained. This type of defect occurs in the highly ionic compounds which posses high co-ordination number and cations and anions of similar sizes. For example CsCl NaCl, KCl, and KBr etc.
(c) The Frenkel defect: This defect arises when the ion is missing from its lattice site and occupies the interstitial position. The crystal as the whole remains electrically neutral in nature because of the number of anions and cations remain the same. Since the cations are generally smaller than the anions, they occupy interstitial sites. This defect occurs in the compounds which posses low co-ordination number and the cations and anions of different sizes.
For example AgCl ZnS, and AgI etc. Frenkel defect are not found in the pure alkali metal halides because cations because of larger size cannot get into the interstitial sites. In the AgBr both the Schottky and Frenkel defects occur at the same time.
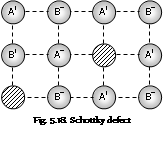
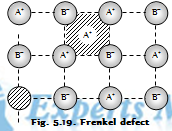
The Consequences of the Schottky and Frenkel defects
The presence of the large number of Schottky defect lowers density of the crystal. When the Frenkel defect alone is present, there is no decrease in its density. The closeness of the charge brought about by the Frenkel defect tends to increase the dielectric constant of crystal. The compounds having this type of defect conduct electricity to the small extent. When the electric field is applied, the ion moves from its lattice site to occupy the hole, it generates a new hole. In this manner, a hole moves from one end to other. Hence, it conducts the electricity across crystal. Because of the presence of holes, the stability (or lattice energy) of the crystal decreases.
(ii) Non-stoichiometric defects : The defects which disturb the stoichiometry of the compounds are called non-stoichiometry defects. These defects are either because of the presence of excess metal ions or deficiency of metal ions.
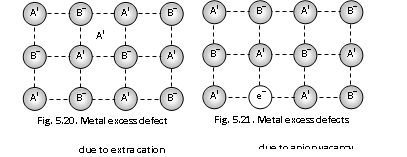
(a) Metal excess defects due to anion vacancies : A compound may have excess metal anion if a negative ion is absent from its lattice site, leaving the hole, which is occupied by an electron to maintain electrical neutrality. These kinds of defects are found in the crystals which are likely to possess the Schottky defects. The Anion vacancies in the alkali metal halides are reduced by heating up the alkali metal halides crystals in an atmosphere of alkali metal vapours. The 'holes' occupy by electrons are called F-centres (or colour centres).
(b) Metal excess defects due to interstitial cations : Another way in which metal excess defects might occur is, if the extra positive ion is present in an interstitial site. Electrical neutrality of it is maintained by the presence of an electron in the interstitial site. This kind of defects are possessed by the crystals which are likely to exhibit Frenkel defects for example when ZnO is heated up, it loses oxygen reversibly. The excess is accommodated in the interstitial sites, with the electrons trapped in neighborhood.
The yellow colour and electrical conductivity of non-stoichiometric ZnO is due to these trapped electrons.
Email based Chemistry assignment help - homework help at Expertsmind
Are you searching chemistry expert for help with Defects or Imperfections in the solids questions? Defects or Imperfections in the solids topic is not easier to learn without external help? We at www.expertsmind.com offer finest service of Chemistry assignment help and chemistry homework help. Live tutors are available for 24x7 hours helping students in their Defects or Imperfections in the solids related problems. We provide step by step Defects or Imperfections in the solids question's answers with 100% plagiarism free content. We prepare quality content and notes for Defects or Imperfections in the solids topic under chemistry theory and study material. These are avail for subscribed users and they can get advantages anytime.
Why Expertsmind for assignment help
- Higher degree holder and experienced experts network
- Punctuality and responsibility of work
- Quality solution with 100% plagiarism free answers
- Time on Delivery
- Privacy of information and details
- Excellence in solving chemistry queries in excels and word format.
- Best tutoring assistance 24x7 hours