Crystal Oscillator:
Some crystals found in nature have the piezoelectric effect which means that when an AC voltage is applied across them, they vibrate at frequency of the applied voltage. Conversely, if they are pressed mechanically, they generate an AC voltage. The main substances which produce the piezoelectric effect are Rochelle salt s, Quartz, and Tourmaline.
The Rochelle salts have greatest piezoelectric activity, for the given AC voltage, they vibrate more than quartz or tourmaline. They are the weakest mechanically, they break easily. They are used in phonograph pickups, microphones, headsets and loudspeakers.
The Tourmaline shows least piezoelectric activity but is a strongest of the 3. It is also the most expensive and used at the very high frequencies.
Quartz is a negotiation between the piezoelectric activity of Rochelle salts and the strength of tourmaline. It is inexpensive and available easily in nature. It is most extensively used for RF oscillators and filters.
Natural shape of a quartz crystal is a hexagonal prism with the pyramids at ends. To get a useable crystal out of this it is sliced in the rectangular slap form of thickness t. The number of slabs we can get from the natural crystal depends on size of the slabs and the angle of cut.
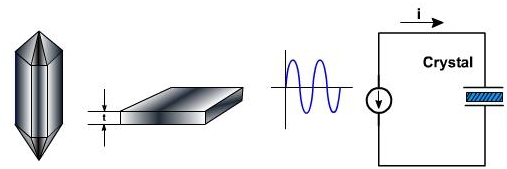
Figure 1
For the use in electronic circuits, slab is mounted in between two metal plates, as shown in the figure 1. In this circuit the amount of crystal vibration depends on the frequency of applied voltage. By changing frequency, one can find resonant frequencies at which the crystal vibrations reach the maximum. Since energy for the vibrations should be supplied by the AC source, the AC current is maximized at each resonant frequency. Most of the time, the crystal is cut and mounted to vibrate best at one of its resonant frequencies, usually fundamental or lowest frequency. Higher resonant frequencies, called as overtones, are almost exact multiplies of fundamental
Frequency for example a crystal with a fundamental frequency of 1 MHz has overtones of 2 MHz, 3MHz and so on. The formula for fundamental frequency of the crystal can be given by
f = K / t.
here K is a constant which depends on the cut and other factors, t is thickness of the crystal, f is inversely proportional to the thickness t. Thinner the crystal, more fragile it becomes and the more likely it is to break because of the vibrations. Quartz crystals can have fundamental frequency up to 10 MHz. To get higher frequencies, a crystal is mounted to vibrate on overtones; we can reach the frequencies up to 100 MHz.
Email based Electronics Devices and circuits assignment help - homework help at Expertsmind
Are you searching Electronics Engineering assignment help expert for help with Crystal Oscillator questions? Crystal Oscillator topic is not easier to learn without any external help? We at www.expertsmind.com offers free lecture notes for Electronics Devices and circuits assignment help and Electronics Devices and circuits homework help. Live tutors are available 24x7 hours for helping students in their Crystal Oscillator related problems. We provide step by step Crystal Oscillator question's answers with 100% plagiarism free content. We prepare quality content and notes for Crystal Oscillator topic under Electronics Devices and circuits theory and study material. These are avail for subscribed users and they can get advantages anytime.
Why Expertsmind for assignment help
- Higher degree holder and experienced experts network
- Punctuality and responsibility of work
- Quality solution with 100% plagiarism free answers
- Time on Delivery
- Privacy of information and details
- Excellence in solving electronics engineering questions in excels and word format.
- Best tutoring assistance 24x7 hours