Covalent radius: It is half of the distance between the nuclei of two like atoms bonded together by a single bond. Therefore covalent radius of carbon in a compound having C - C single bond can be determined by dividing bond length by 2, that is
Rc = (c-c)/2 Thus, C-C = 2rc or rc + rc
here, is the single bond covalent radii ( which is SBCR) of carbon. Though, if atoms forming the covalent bond are different that is one is more electronegative than the other then the atomic radius can be determined by the relation
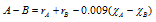
here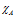 and
and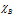 are electronegativities of the atoms A and B respectively. The relation was given by the scientist Stevenson in the year 1941.
are electronegativities of the atoms A and B respectively. The relation was given by the scientist Stevenson in the year 1941.
In the given period, atomic radius usually decreases from left to right and hence in any of the period, alkali metal is the largest and halogen is the smallest atom. For instance, in second period elements the covalent radii decrease from Li to F.
|
3Li
1.23
|
4Be
0.89
|
5B
0.80
|
6C
0.77
|
7N
0.74
|
8O
0.74
|
9F
0.72
|
10Ne
1.6
|
The decrease in size along a period is due to the effect of successive increasing nuclear charge without addition of a new shell, that is in each element of a given period a new electron is added in the same principal quantum number. For instance, in the second period the nuclear charge increases from + 3 in Li to + 9 in F. The increased nuclear charge attracts the electrons more strongly to the nucleus and thus decreases the size of the atom. In the case of noble gases, atomic radii are only the vander Waal's radii which are naturally higher than the covalent radii of other elements.
In a given group, Atomic radius generally increases as one moves from top to bottom, for example in group 1 atomic size increases steadily from the lithium to cesium, which can be given as 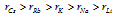
The increase in size on descending a group is due to addition of extra shell which outweighs the effect of increased nuclear charge. Keep in mind that He and Fr are smallest and largest atom respectively.
Email based Chemistry assignment help - homework help at Expertsmind
Are you searching chemistry expert for help with Covalent radius questions? Covalent radius topic is not easier to learn without external help? We at www.expertsmind.com offer finest service of Chemistry assignment help and chemistry homework help. Live tutors are available for 24x7 hours helping students in their Covalent radius related problems. We provide step by step Covalent radius question's answers with 100% plagiarism free content. We prepare quality content and notes for Covalent radius topic under chemistry theory and study material. These are avail for subscribed users and they can get advantages anytime.
Why Expertsmind for assignment help
- Higher degree holder and experienced experts network
- Punctuality and responsibility of work
- Quality solution with 100% plagiarism free answers
- Time on Delivery
- Privacy of information and details
- Excellence in solving chemistry queries in excels and word format.
- Best tutoring assistance 24x7 hours