Copper:
Types of Ores
- Copper pyrites (chalcopyrite) CuFeS2,
- Cuprite (ruby copper) Cu2O,
- The Copper glance Cu2S ,
- Malachite [Cu(OH)2.CuCO3],
- Azurite [Cu(OH)2.2CuCO3]
Extraction of Copper
Most of the copper which is approximately 75% is extracted from the sulphide ore, copper pyrites of it.
Concentration of ore: Froth floatation procedure.
Roasting: Main reaction of this is as follow:
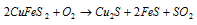 .
.
Side reaction:
The reaction for it is as follow:
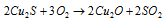
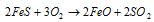 .
.
Smelting:
Smelting is explained like this:
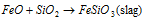
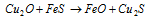
Mixture of the copper and iron sulphides melt jointly to make 'matte' (Cu2S + FeS) and the slag floats on its surface.
Conversion of matte into Blister copper (Bessemerisation)
Silica is added to matte and a hot blast of air is passed FeO + SiO2 → FeSiO3 (slag). After that the Slag is removed. By this time most of iron sulphide is eliminated. Cu2S + 2Cu2O→6Cu + SO2
Blister copper
Blister copper consists of approximately 98% pure copper and the rest that is only 2% impurities (Ag, Au, Ni, Zn etc.)
Physical Properties of copper:
The properties of copper are as follow:
(1) Copper has reddish brown colour.
(2) Copper is very malleable and ductile.
(3) Copper as well has high electrical conductivity and high thermal conductivity.
(4) Copper is the second most helpful metal because the first is iron.
(5) Copper goes through the displacement reactions with lesser reactive metals example for this is, with Ag.
(6) Copper can displace Ag from AgNO3 . The at last divided Ag so acquired is black in colour.
Copper exhibit oxidation states of +1 and +2. While copper (I) salts are colorless, copper (II) in color salts are blue. Cu (I) salts are very much less stable and therefore are simply oxidized to Cu (II) salts (2Cu → Cu2+ + Cu). This reaction is termed as disproportionation.
(A) In existence of atmospheric CO2 and moisture, copper gets covered with a green layer of basic copper carbonate (green layer) that protects the rest of the metal from additional action.
Equation that explained it is as follow:
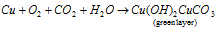
(B) In existence of oxygen or air, copper heated to the redness (beneath temperature 1370 Kelvin) very firstly forms red cuprous oxide that alters to black cupric oxide on further heating. If the temperature is extremely high, cupric oxide (Cu2O) changes back to the cuprous oxide
Equation:
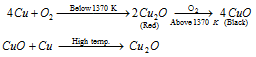
(C) Action of acids. Non oxidising dil. acids like HCl, H2SO4 have no action on copper. Even though, copper dissolves in these acids in existence of air.
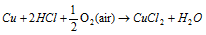
With dilute HNO3, Cu liberates NO (nitric oxide) the equation is:
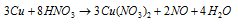
With concentrated HNO3, copper gives NO2 the equation is:
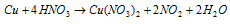
With hot concentrated H2SO4, copper gives SO2 the equation is:
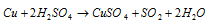
Email based Chemistry assignment help - homework help at Expertsmind
Are you searching chemistry expert for help with Copper questions? Copper topic is not easier to learn without external help? We at www.expertsmind.com offer finest service of Chemistry assignment help and chemistry homework help. Live tutors are available for 24x7 hours helping students in their Copper related problems. We provide step by step Copper question's answers with 100% plagiarism free content. We prepare quality content and notes for Copper topic under chemistry theory and study material. These are avail for subscribed users and they can get advantages anytime.
Why Expertsmind for assignment help
- Higher degree holder and experienced experts network
- Punctuality and responsibility of work
- Quality solution with 100% plagiarism free answers
- Time on Delivery
- Privacy of information and details
- Excellence in solving chemistry queries in excels and word format.
- Best tutoring assistance 24x7 hours