Concentration or dressing of the ore: The ore are usually obtained from the ground and therefore contained large amount of unwanted impurities, such as rocky matter, earthing particles, sand, limestone etc. These impurities are known collectively as gangue or matrix. It is important to separate the large bulk of these impurities from the ore to avoid bulk handling and in subsequent fuel costs. The elimination of these impurities from the ores is known as concentration. The concentration of it is done by the physical as well as chemical methods.
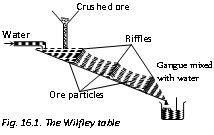
Physical Methods (i) Gravity Separation or levigation: This process of concentration is based on the difference in the specific gravity of the ore and gangue. The sieved ore is subjected to dry centrifugal separation or is placed in big shallow tanks in which a strong current of water blows. Heavy and large ore particles settle down to the bottom of the tanks while lighter gangue particles are carried away by the current of water. The process eliminates most of the soluble and insoluble impurities. For this reason wilfley table and hydraulic classifier are broadly used. The method is specifically suitable for heavy oxide and carbonate ores like Cassiterite (SnO2) and haematite.
(ii) Froth floatation process : In some cases for instance, sulphides ores of copper, lead and zinc concentration is brought by this process. In this process advantage is taken of the preferential wetting of the ore by oil. The properly ground and crushed ore is taken in a tank containing water and 1% of pine oil or terpentine oil. A powerful current of air is blown through the suspension, forming a heavy froth or foam on the surface. The metal sulphide is drenched by the oil but the gangues is not and the sulphide-oil mixture is carried to the surface by films of oil The froth is skimmed off, the gangue or waste settles down on the bottom or remains underneath the froth. By this floatation process it is possible to concentrate over 90% of a sulphite ore to 1/10 of its original bulk.
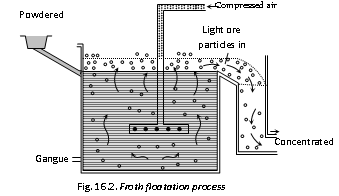
(ii) Activators and Depressants : During the floatation process of some ores, the substances are added which activate or depress floatation property of the minerals and thus help in the separation of minerals present in the ore. For instance, galena (PbS) is usually associated with sphalerite (ZnS) and pyrites (FeS2). Concentration of galena is carried out by passing potassium ethyl xanthate (Collector) along with sodium cynamide and alkali (depressants) whereby the floatation property of ZnS and FeS2 is depressed. Specifically PbS passes into the froth when air current in flown in, and is collected. After PbS is eliminated with the froth, same CuSO4 (activator) is added and air is blown. The floting property of ZnS is increased which is now removed with froth. The slurry is acidified and method is repeated when FeS2 passed into the froth and is collected.
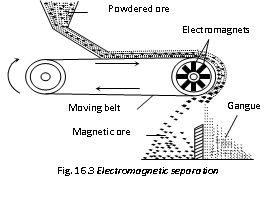
(iii) Electromagnetic separation : If the mineral and not gangue is attracted by a magnet, it can be concentrated by magnetic separation. For instance chromite ore, FeCr2O4 being magnetic can be separated from non-magnetic silicons impurities by this method. Sometimes two minerals occur together, in which one happens to be magnetic. By magnetic separation method the nonmagnetic minerals is separated from the magnetic mineral. For example tin-stone or cassiterite, SnO2 (non-magnetic) containing wolfram, FeWO4 (magnetic) is separated by this method. In this method a thin layer of finely ground ore is spread over a rubber belt carried over a pulley in a magnetic field. The gangue particles or the particles of non-magnetic mineral fall off as the belt becomes vertical, and the magnetic particles collect.
Chemical methods
(i) Calcination : This is the process in which the concentrated ore is heated in a suitable furnace generally in reveratory furnace below its melting point in absence of air. As a result of which the ore dries up and moisture and volatile impurities are driven off and carbonates are converted into oxides and the ore becomes porous. For example,
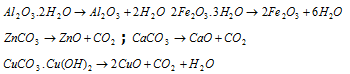
(ii) Roasting : The process of heating the ores strongly in presence of air with or without certain substances, below its melting point is called as roasting. It varies from calcination in respect that the heating is done in presence of air and at the higher temperature. In this procedure the impurities of sulphur and arsenic are volatilized as oxides and the ore is converted into the oxide. For instance zinc oxide is formed by the oxidation of zinc blende,
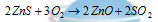
(iii) Leaching : It involves the treatment of the ore with a suitable reagent as to make it soluble while impurities remain insoluble. The ore can be recovered from solution by the appropriate chemical method. For instance, the chief ore of aluminium, bauxite (Al2O3.2H2O) contains varying amounts of titanium oxide ferric oxides, and silica. As alumina is amphoteric, it can be removed from the other two oxides. Finely crushed and powdered bauxite is digested with caustic soda solution at 150-170oC under the pressure for some hours. Alumina dissolves forming the soluble sodium aluminate.
Al2O3. 2H2O + 2NaOH → 2NaAlO2 + 3H2O
The impurities remain as it is and separated as insoluble red mud which is filtered off. The filtrate is diluted and some freshly precipitated aluminium hydroxide is added when Al(OH)3 is precipitated as shown below,
NaAlO2 + 2H2O → NaOH + Al(OH)3
After that the precipitated hydroxide is then filtered off and calcified to get highly pure aluminium oxide (alumina).
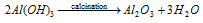
Gold and silver can also be extracted from their native ores by Leaching (Mac-Arthur forest cyanide process).
Email based Chemistry assignment help - homework help at Expertsmind
Are you searching chemistry expert for help with Concentration and dressing of the ore questions? Concentration and dressing of the ore topic is not easier to learn without external help? We at www.expertsmind.com offer finest service of Chemistry assignment help and chemistry homework help. Live tutors are available for 24x7 hours helping students in their Concentration and dressing of the ore related problems. We provide step by step Concentration and dressing of the ore question's answers with 100% plagiarism free content. We prepare quality content and notes for Concentration and dressing of the ore topic under chemistry theory and study material. These are avail for subscribed users and they can get advantages anytime.
Why Expertsmind for assignment help
- Higher degree holder and experienced experts network
- Punctuality and responsibility of work
- Quality solution with 100% plagiarism free answers
- Time on Delivery
- Privacy of information and details
- Excellence in solving chemistry queries in excels and word format.
- Best tutoring assistance 24x7 hours