Compounds of calcium
(i) Calcium oxide or Quick lime or Burnt lime (CaO) : It's aqueous suspension is known as slaked lime.
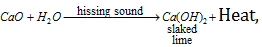
It is when exposed to the oxy-hydrogen flame, it starts emitting light called lime light.
CaO is used as aflux, for removing the hardness of water, as a drying agent (for NH3 gas) for preparing mortar (CaO+ sand +water).
Mortar : Mortar used in making buildings is a mixture of lime (CaO) and sand in the ratio 1 : 3 with enough water to make a thick paste. When the mortar is placed between bricks, it slowly absorbs CO2 from the air and the slaked lime revers to CaCO3.
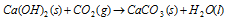
However, the sand in the mortar is chemically inert, the grains are bound together by the particles of calcium carbonate and a hard material results.
(ii) Calcium chloride (CaCl2.6H2O), Fused CaCl2 is a good dessicant (drying agent). It can't be used to dry alcohol or ammonia as it forms additional products with them.
(iii) Calcium carbonate (CaCO3) :
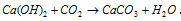
It is insoluble in water but dissolves in the presence of CO2 due to the formation of calcium bicarbonate.
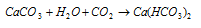
It is ingredient of the protective shells of marine animals.
(iv) Gypsum (CaSO4.2H2O) - On partially dehydrates to produce plaster of paris.

Plaster of paris :
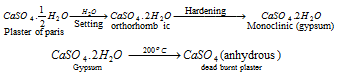
Gypsum when heated to about 200oC is converted into anhydrous calcium sulphate. The anhydrous form (anhydrite) is known as dead burnt plaster because it does not set like plaster of paris when moistened with water.
(v) Calcium Hydroxide Ca(OH)2 (slaked lime)
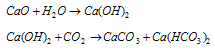
Suspension of Ca(OH)2 in water is called milk of lime.
(vi) Cement : (a) It is essentially a mixture of lime stone and clay. It is also called Portland cement because in presence of water it sets to a hard stone-like mass resembling with the famous Portland rock, a famous building stone of England. The approximate composition of cement is
Calcium oxide (CaO) 50 - 60 %
Silica (SiO 2) 20 - 25%
Alumina (Al2O3) 5 - 10%
Magnesia (MgO) 1 - 3%
Ferric oxide (Fe2O3 ) 1 - 3%
The above compounds are provided by the two raw materials, namely lime stone (which provides CaO) and clay which provides SiO2, Al2O3 and Fe2O3. In cement, almost entire amount of lime is present in the combined state as calcium silicates (2CaO.SiO2 and 3CaO.SiO2) and calcium aluminates (3CaO.Al2O3 and 4CaO.Al2O3).
(b) Cement containing excess amount of lime cracks during setting; while cement containing less amount of lime is weak in strength.
(c) Cement with excess of silica is slow-setting and that having an excess of alumina is quick-setting.
(d) Cement containing no iron oxide is white but hard to burn.
Cement is manufactured by two processes, viz, wet and dry. A small amount (2-3%) of gypsum is added to slow down the setting of the cement so that it gets sufficiently hardened. Setting of cement is an exothermic process and involves hydration of calcium aluminates and calcium silicates.
Email based Chemistry assignment help - homework help at Expertsmind
Are you searching chemistry expert for help with Compounds of Calcium questions? Compounds of Calcium topic is not easier to learn without external help? We at www.expertsmind.com offer finest service of Chemistry assignment help and chemistry homework help. Live tutors are available for 24x7 hours helping students in their Compounds of Calcium related problems. We provide step by step Compounds of Calcium question's answers with 100% plagiarism free content. We prepare quality content and notes for Compounds of Calcium topic under chemistry theory and study material. These are avail for subscribed users and they can get advantages anytime.
Why Expertsmind for assignment help
- Higher degree holder and experienced experts network
- Punctuality and responsibility of work
- Quality solution with 100% plagiarism free answers
- Time on Delivery
- Privacy of information and details
- Excellence in solving chemistry queries in excels and word format.
- Best tutoring assistance 24x7 hours