|
Property
|
Diamagnetic substances
|
Paramagnetic substances
|
Ferromagnetic substances
|
|
Cause of magnetism
|
Orbital movement of electrons
|
Spin motion of electrons
|
Formation of domains
|
|
Explanation of magnetism
|
On the basis of orbital motion of electrons
|
On the basis of spin and orbital motion of electrons
|
On the basis of domains formed
|
|
Behavior In a non-uniform magnetic field
|
These are repelled in an external magnetic field i.e. have a tendency to go from high to low field region.
|
These are feebly attracted in an external magnetic field i.e., have a tendency to go from low to high field region
|
These are strongly attracted in an external magnetic field i.e. they easily go from low to high field region
|
|
State of magnetization
|
These are weekly magnetized in a direction opposite to that of applied magnetic field
|
These get weekly magnetized in the direction of applied magnetic field
|
These get strongly magnetized in the direction of applied magnetic field
|
|
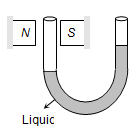
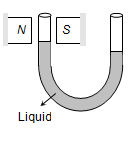
When the material in the form of liquid is filled in the U-tube and placed between pole pieces.
|
Liquid level in that limb goes depressed
|
Liquid level in that limb arises up
|
Liquid level in that limb arises up very much
|
|
On placing the gaseous materials between pole pieces
|
The gas expands at right angles to the magnetic field.
|
The gas expands in the direction of magnetic field.
|
The gas rapidly expands in the direction of magnetic field
|
|
The value of magnetic induction B
|
B < B0
|
B > B0
|
B >> B0
|
|
Magnetic susceptibility c
|
Low and negative |X| » 1
|
Low but positive X » 1
|
Positive and high X » 102
|
|
Dependence of c on temperature
|
Does not depend on temperature (except Bi at low temperature)
|
Inversely proportional to temperature x∝1/T or x=C/T This is called Curie law, where C = Curie constant
|
x∝1/T-Tc or x=C/T-Tc This is called Curie Weiss law.
Tc = Curie temperature
|
|
Dependence of c on H
|
Does not depend independent
|
Does not depend independent
|
Does not depend independent
|
|
Relative
permeability (mr)
|
μr < 1
|
μr > 1
|
μr >> 1
mr = 102
|
|
Intensity of magnetization (I)
|
I is in a direction opposite to that of H and its value is very low
|
I is in the direction of H but value is low
|
I is in the direction of H and value is very high.
|
|
I-H curves
|
|
|
|
|
Magnetic moment (M)
|
The value of M is very low (» 0 and is in a direction opposite to H.)
|
The value of M is very low and is in the direction of H
|
The value of M is very high and is in the direction of H
|
|
Transition of substances (at Curie temperature)
|
These do not change.
|
On cooling, these get converted to ferromagnetic materials at Curie temperature
|
These get changed into paramagnetic materials above Curie temperature
|
|
The property of magnetism
|
Diamagnetism is found in those materials the atoms of which have even number electrons
|
Para magnetism is found in those materials the atoms of which have majority of electron spins in the same direction
|
Ferro-magnetism is found in those materials which when placed in an external magnetic field are strongly magnetized
|
|
Examples
|
Cu, Ag, Au, Zn, Bi, Sb, NaCl, H2O air and diamond etc.
|
Al, Mn, Pt, Na, CuCl2, O2 and crown glass
|
Ni, Co, Fe, Fe3O4, Cd etc.
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|