Common mode Gain:
A common mode signal is one which drives both inputs of the differential amplifier equally. The common mode signal is interference, static and other types of the undesirable pickup etc.
The connecting wires on input bases act as small antennas. If the differential amplifier is operating in the environment with lot of electromagnetic interference, each base picks up an unwanted interference voltage. If both transistors were matched in all respects then balanced output would be theoretically zero. This is the significant characteristic of the differential amplifier. It discriminates against the common mode input signals. Or we can say that it refuses to amplify common mode signals.
The practical effectiveness of rejecting common signal depends on degree of matching in between 2 CE stages forming the differential amplifier. Or we can say that more closely are the currents in input transistors, the better will be the common mode signal rejection for example If v1 and v2 are 2 input signals, then the output of a practical op-amp cannot be described by simply
v0 = Ad (v1 - v2 )
In practical differential amplifier, output relies not only on the difference signal but also on the common mode signal
vd = (v1 - vd )
and vC = ½ (v1 + v2 )
The output voltage, hence can be expressed as vO = A1 v1 + A2 v2
Here A1 & A2 are voltage amplification from input 1(2) to output under condition that input 2 (1) is grounded.
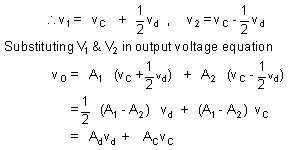
The voltage gain for difference signal is Ad and for common mode signal is AC.
The ability of a differential amplifier to reject a common mode signal can be expressed by its common mode rejection ratio (CMRR). This is the ratio of differential gain Ad to common mode gain AC.
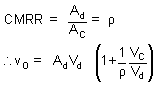
The date sheet always specifies the CMRR in decibels CMRR = 20 log CMRR.
Thus, the differential amplifier should be designed so that r is quite large as compared with the ratio of common mode signal to difference signal. If r = 1000, vC = 1mV, vd = 1 m V, then
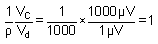
This is equal to the first term. Thus for the amplifier with r = 1000, a 1m V difference of the potential between the 2 inputs gives the same output as 1mV signal applied with same polarity to both the inputs.
Email based Electronics Devices and circuits assignment help - homework help at Expertsmind
Are you searching Electronics Engineering assignment help expert for help with Common mode Gain questions? Common mode Gain topic is not easier to learn without any external help? We at www.expertsmind.com offers free lecture notes for Electronics Devices and circuits assignment help and Electronics Devices and circuits homework help. Live tutors are available 24x7 hours for helping students in their Common mode Gain related problems. We provide step by step Common mode Gain question's answers with 100% plagiarism free content. We prepare quality content and notes for Common mode Gain topic under Electronics Devices and circuits theory and study material. These are avail for subscribed users and they can get advantages anytime.
Why Expertsmind for assignment help
- Higher degree holder and experienced experts network
- Punctuality and responsibility of work
- Quality solution with 100% plagiarism free answers
- Time on Delivery
- Privacy of information and details
- Excellence in solving electronics engineering questions in excels and word format.
- Best tutoring assistance 24x7 hours