Chemical properties of Ether : Ethers are quite stable compounds. These are not easily reacted with dilute mineral acids, active metals, alkalies, oxidising agents under ordinary conditions or reducing agents.
(1) Reaction due to alkyl group
(i) Halogenation :
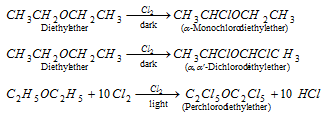
(ii) Burning : Ethers are highly inflammable. They burn like alkanes.
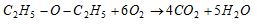
(2) Reaction due to ethernal oxygen
(i) Peroxide formation :
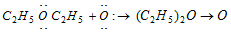 .
.
(a) The boiling point of peroxide is higher than that of ether. It is absent as remains in the distillation of ether and may cause explosion. Therefore ether can never be vaporized to dryness.
(b) Absolute ether can be prepared by distillation of ordinary ether from conc. H2SO4 and subsequent storing over metallic sodium.
- Generation of peroxide can be prevented by adding small amount of Cu2O to ether.
- With strong oxidising agent like dichromate ethers, acid are oxidised to aldehydes.
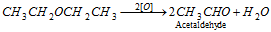
- The existence of peroxide can be shown by the formation of blood red colour complex in the following reaction.
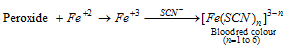
(ii) Oxidation with K2Cr2O7 / HÅ
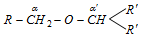
(a) Oxidation of ether can only be possible if any one of the alkyl groups of ether has hydrogen on a-carbon.
(b) a-carbon having two hydrogens converts in carboxylic group and a-carbon having only one hydrogen converts into keto group.
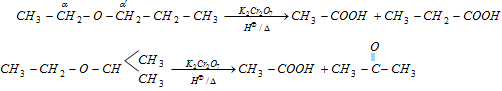
(iii) Salt formation : Due to lone pair of electrons on oxygen molecules. Ether acts as Lewis base and form stable oxonium salt with strong inorganic acids at low temperature.
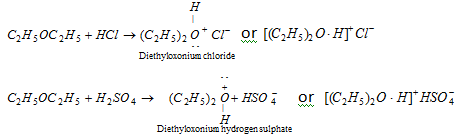
The oxonium salts are soluble in acid solution and ethers can be recovered from the oxonium salts by treatment with water.
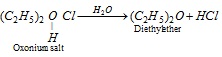
- The formation of oxonium salt is same to the formation of ammonium salts from ammonia and acids.
- Ether is removed from alkyl halides by shaking with conc.H2SO4.
- Ethers may be categorized from alkanes with the help of this reaction.
(3) Reaction involving cleavage of carbon-oxygen bond
(i) Hydrolysis
(a) With dil. H2SO4 : 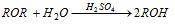
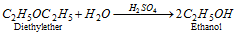
(b) With conc.H2SO4 :
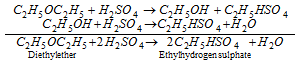
(ii) Zeisel method : 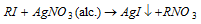
- The silver iodide thus form can be estimated and detected. This is the basis of Zeisel process for the estimation and detection of alkoxy group in a compound.
(4) Ring substitution in aromatic ethers : Alkoxy group is ortho and para directing and it directs the incoming groups to ortho and para position. It turns on the aromatic ring leads to electrophilic substitution reaction.

III, IV and V indicates high electron density at ortho and para position.
(i) Halogenation : Phenyl alkyl ethers undergo usual halogenation in benzene ring.
For example, Bromination of anisole gives ortho and para bromo derivative even in the absence of iron (III) bromide catalyst.
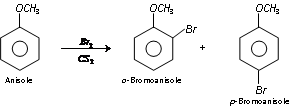
Para isomer is obtained in 90% yield.
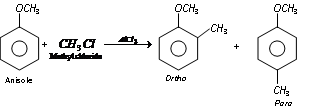
(ii) Friedel craft reaction
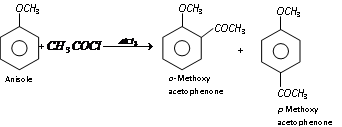
(iii) Nitration
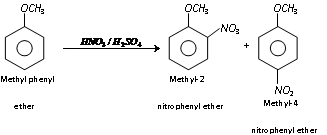
- Ethers are relatively less reactive than phenol towards electrophilic substitution reaction.
Email based Chemistry assignment help - homework help at Expertsmind
Are you searching chemistry expert for help with Chemical Properties of Ether questions? Chemical Properties of Ether topic is not easier to learn without external help? We at www.expertsmind.com offer finest service of Chemistry assignment help and chemistry homework help. Live tutors are available for 24x7 hours helping students in their Chemical Properties of Ether related problems. We provide step by step Chemical Properties of Ether question's answers with 100% plagiarism free content. We prepare quality content and notes for Chemical Properties of Ether topic under chemistry theory and study material. These are avail for subscribed users and they can get advantages anytime.
Why Expertsmind for assignment help
- Higher degree holder and experienced experts network
- Punctuality and responsibility of work
- Quality solution with 100% plagiarism free answers
- Time on Delivery
- Privacy of information and details
- Excellence in solving chemistry queries in excels and word format.
- Best tutoring assistance 24x7 hours