Chemical properties
(1) The formation of oxides and hydroxides can be understood as follows
(i) These are the most reactive metals and having strong affinity towards O2 quickly tarnish in the air due to the formation of a film of their oxides on the surface. These are, hence, kept under kerosene or paraffin oil to protect them from the air,
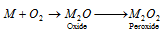
(ii) When burnt air (O2), lithium forms lithium oxide (Li2O) sodium forms sodium peroxide (Na2O2) and other alkali metals form super oxide (Mo2 i.e. KO2,RbO2 or CsO2)
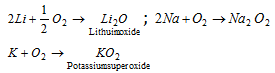
The reactivity of alkali metals towards oxygen to form different oxides is due to strong positive field around each alkali metal cation. Li+ being smallest, possesses strong positive field and thus combines with small anion O2- to form stable Li2O compound. The Na+ and K+ being relatively larger thus exert less strong positive field around them and thus reacts with larger oxygen anion i.e, O22- and O21- to form stable oxides.
The monoxide, peroxides and superoxides have O2 and O22- , O21- ions respectively. The structures of each can be under stood as follows,
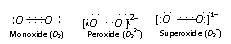
The O2-1 ion has a three electron covalent bond and has one electron unpaired. It is hence superoxides are paramagnetic and coloured KO2 is light yellow and paramagnetic substance.
(iii) Oxides of the alkali metals and metal itself give the strongly alkaline solution in water with the evolution of heat
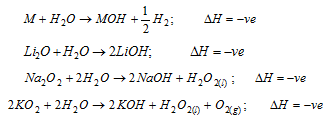
The peroxides and the superoxides act as strong oxidising agents because of the formation of H2O2
(iv) The reactivity of alkali metals towards air and water increases from Li to Cs that is why lithium decomposes H2O very slowly at 25oC whereas Na does so vigorously, K reacts giving a flame and Rb, Cs is explosive.
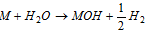
(v) The basic character of oxides and hydroxides of alkali metals increases from Li to Cs. This is because of the increase in ionic character of alkali metal hydroxides down the group which leads to complete dissociation and leads to increase in concentration of OH- ions.
(2) Hydrides
(i) These metals combine with H to give white crystalline ionic hydrides of the general of the formula MH.
(ii) The tendency to form their hydrides, basic nature and stability decreases from the Li to Cs since electropositive character decreases from the Cs to Li.
2M+ H2 → 2MH ; The reactivity towards H2 is Cs < Rb < K < Na < Li.
(iii) The metal hydrides react with the water to provide MOH and H2 ; MH + H2 O → MOH + H2
(iv) The ionic nature of the hydrides increases from Li to Cs due to the fact that the hydrogen is present in these hydrides as H- and smaller cation will produce more polarisation of the anion (in accordance to Fajans rule) and will develop more covalent character.
(v) The electrolysis of the fused hydrides give H2 at anode 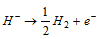 .
.
NaHfused Contains Na+ and H- i.e.,
At cathode: Na+ +e- → Na; At anode:
(vi) Alkali metals form hydrides such as NaBH4, LiAlH4 which are effective reducing agent.
(3) Carbonates and Bicarbonates
(i) The carbonates (M2CO3) & the bicarbonates (MHCO3) are highly stable to heat, here M stands for the alkali metals.
(ii) The stability of these salts increases with the increase in electropositive character from Li to Cs. It is thus Li2CO3 decompose on heating, Li2CO3 → Li2O+CO2
(iii) The bicarbonates are decomposed at the relatively low temperature, 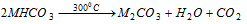
(iv) Carbonates and bicarbonates both are soluble in water to give alkaline solution because of hydrolysis of carbonate ions or the bicarbonate ions.
(4) Halides
(i) Alkali metals combine directly with the halogens to form ionic the halide M+X- .
(ii) The ease with which the alkali metals form halides increases from Li to Cs due to increasing electropositive character from Li to Cs.
(iii) Lithium halides however have more covalent nature. The smaller is the cation, more is deformation of the anion and hence more is covalent nature in compound. Also among the lithium iodide lithium halides, has maximum covalent nature because of larger anion which is simply deformed by a cation. Hence covalent character in lithium halides can be given as, LiI > LiBr > LiCl > LiF
(iv) These are readily soluble in water. Although, lithium fluoride is sparingly soluble. The low solubility of LiF is because of higher forces of attractions among smaller Li+ and smaller F- ions (high lattice energy).
(v) Halides having ionic nature have high melting point and good conductor of current. The melting points of the halides shows the order, NaF > NaCl > NaBr > Nal
(vi) Halides of potassium, rubidium and caesium have a property of combining with extra halogen atoms forming the polyhalides.
KI + I2 ®KI3; In KI3(aq) the ions K+ and I-3 are present
(5) Solubility in liquid NH3
(i) These type of metals dissolve in liquid NH3 to obtain blue coloured solution, which conducts electricity to the appreciable degree.
(ii) The increasing concentration of the ammonia, blue colour begins changing to that of metallic copper after which the dissolution of alkali metals in NH3 stops.
(iii) The metal atom is converted into the ammoniated metal in that is M+ (NH3) and the electron set free combines with NH3 molecule to produce ammonia solvated electron.
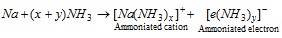
(iv) It is the ammoniated electron which is responsible for blue colour, reducing power and paramagnetic nature of alkali metals in ammonia solution. Although, increased conductance nature of these metals in ammonia is because of presence of the ammoniated cation and ammonia solvated electron.
(v) The stability of the metal-ammonia solution decreases from Li to Cs.
(vi) The blue solution on standing or on the heating slowly liberates hydrogen, 2M + 2NH3 ® 2MNH2 + H2. The Sodamide (NaNH2) is a waxy solid, which is used in preparation of the number of sodium compounds.
(6) Nitrates : Nitrates of the alkali metals (MNO3) are soluble in water and decompose on heating. LiNO3 decomposes to provide NO2 and O2 and rest all provide nitrites and oxygen.
2MNO3 → 2MNO2 + O2 (except Li)
4 LiNO3 → 2Li2O + 4NO2 + O2
(7) Sulphates
(i) The sulphate of alkali metal have the formula M2SO4 .
(ii) Except Li2SO4, rest all are soluble in water.
(iii) These sulphates on fusing with carbon form sulphides, M2SO4 + 4C → M2S + 4CO
(iv) The sulphates of alkali metals (except Li) form double salts with the sulphate of the trivalent metals such as Fe, Al, Cr and many more The double sulphates crystallize with large number of water molecules as alum. For example K2SO4 . Al2 (SO4)3. 24 H2O.
(8) Reaction with non-metals
(i) These have high affinity for non-metals. Except for the carbon and nitrogen, they directly react with halogens, sulphur, phosphorus hydrogen, etc. to form the related compounds on heating.
2Na + H2 →2NaH ; 2K + H2 → 2KH
2Na + Cl2 → 2NaCl ; 2K + Cl2 → 2KCl
2Na + S → Na2S ; 2K + S → K2S
3Na + P → Na3P ; 3K + P → K3P
(ii) Li reacts, however directly with carbon and nitrogen to form carbides and nitrides.
2Li + 2C → LiC2 ; 6Li + 2N2 → 2 Li3N
(iii) The nitrides of these metals on reaction with water give NH3.
M3N + 3H2O → 3MOH + NH3
(9) Reaction with acidic hydrogen : Alkali metals react with acids and other compounds containing acidic hydrogen (i.e, H atom attached on F,O, N and triply bonded carbon atom, for example, HF, H2O, ROH, RNH2, CH º CH) to liberate H2 .
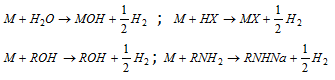
(10) Complex ion formation : A metal shows complex formation only when it possesses the following characteristics,
(i) Small size
(ii) High nuclear charge
(iii) Presence of empty orbitals in order to accept electron pair ligand.
Only Lithium in the alkali metals because of small size forms a few complex ions Rest all alkali metals do not possess the tendency to form complex ion.
Email based Chemistry assignment help - homework help at Expertsmind
Are you searching chemistry expert for help with Chemical Properties of Alkali Metals questions? Chemical Properties of Alkali Metals topic is not easier to learn without external help? We at www.expertsmind.com offer finest service of Chemistry assignment help and chemistry homework help. Live tutors are available for 24x7 hours helping students in their Chemical Properties of Alkali Metals related problems. We provide step by step Chemical Properties of Alkali Metals question's answers with 100% plagiarism free content. We prepare quality content and notes for Chemical Properties of Alkali Metals topic under chemistry theory and study material. These are avail for subscribed users and they can get advantages anytime.
Why Expertsmind for assignment help
- Higher degree holder and experienced experts network
- Punctuality and responsibility of work
- Quality solution with 100% plagiarism free answers
- Time on Delivery
- Privacy of information and details
- Excellence in solving chemistry queries in excels and word format.
- Best tutoring assistance 24x7 hours