Characteristics of hydrocarbons
(1) Knocking : The metallic sound during working of an internal combustion engine is termed as knocking.
"The greater the compression greater will be efficiency of engine." The fuel with minimum knocking characteristic is always preferred.
The tendency to knock falls off in the given sequence : Straight chain alkanes > branched chain alkanes > olefins > cyclo alkanes > aromatic hydrocarbons.
(2) Octane number : It is used for measuring the knocking character of fuel used in petrol engine. The octane quantity of a provided sample can be defined as the percentage by volume of iso-octane present in a mixture of iso-octane and n-heptane which has the same knocking performance as the fuel itself.
CH3 - CH2 - CH2 - CH2 - CH2 - CH3
n-heptane; octane no. = 0
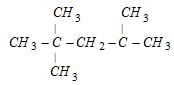 ; Octane no. = 100
; Octane no. = 100
Iso-octane or 2, 2, 4-Trimethyl pentane.
For example : a given sample has the knocking performance equivalent to a mixture containing 60% iso-octane and 40% heptane. The octane number of the gasoline is 60.
Presence of given types of elements adds to the octane number of gasoline.
(i) In case of straight linear chain hydrocarbons octane number decreases with increase in the length of the chain.
(ii) Branching of chain add to the value of octane number
(iii) Introduction of triple bond or double bond adds to the value of octane number.
(iv) Cyclic alkanes have relatively higher value of octane number.
(v) The octane value of aromatic hydrocarbons is exceptionally high
(vi) By adding gasoline additives (eg TEL)
(3) Antiknock compounds : To reduce the knocking property or to improve the octane number of a fuel certain chemicals are included in it. These are known as antiknock compounds. One such substance, which is extensively used, is tetraethyl lead (TEL). TEL is used in the form of following mixture,
TEL = 63%, Ethylene bromide = 26%, Ethylene chloride = 9% and a dye = 2%.
However, there is a disadvantage that the lead is deposited in the engine. To eliminate the free lead, the ethylene halides are added which combine with lead to form volatile lead halides.
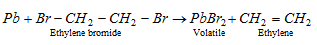
However, utilize of TEL in petrol is facing a harder problem of Lead pollution, to avoid this a new compound cyclopenta dienyl manganese carbonyl (called as AK-33-X) is used in developed countries as antiknocking compound.
(4) Other methods of improving octane number of hydrocarbon.
(i) Isomerisation [Reforming] : By passing an alkane over AlCl3 at 200oC.
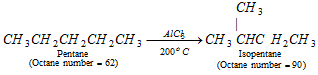
(ii) Alkylation :
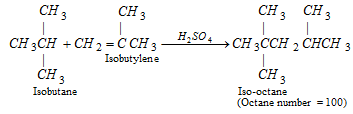
(iii) Aromatisation :
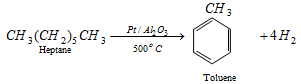
The octane no. of petrol can thus be improved.
· By adding the proportion of branched chain or cyclic alkanes.
· By adding of aromatic hydrocarbons Benzene, Toluene and Xylene (BTX).
· By addition of methanol or ethanol.
· By adding up of tetraethyl lead
(5) Cetane number : It is used for grading the diesel oils.
Cetane → cetane no. = 100
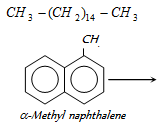 cetane no. = 0
cetane no. = 0
The cetane value of a diesel oil is the percentage of cetane (hexadecane) by volume in a mixture of cetane and α-methyl naphthalene which has the same ignition property as the fuel oil under consideration.
(6) Flash point : The minimum temperature at which an oil gives sufficient vapours to form an explosive mixture with air is referred to as flash point of the oil.
The flash point in India is fixed at 44oC, in France it is fixed at 35oC, and in England at 22.8oC. The flash point of an oil is usually determined by means of "Abel's apparatus".
Chemists have prepared some hydrocarbons with octane number even less than zero (e.g., n-nonane has octane number - 45) as well as hydrocarbon with octane number bigger than 100 (e.g., 2, 2, 3 trimethyl-butane. has octane number of 124).
(7) Petrochemicals : All such chemicals which are derived from petroleum or natural gas called petrochemicals. Some chemicals which are found from petroleum are summarized in table :
Table : 24.2
Hydrocarbons
|
Compounds derived
|
|
Methane
|
Methyl chloride, methanol, chloroform, formaldehyde, formic acid, freon, hydrogen for synthesis of ammonia.
|
|
Ethane
|
Ethyl chloride, acetic acid, ethyl bromide, acetaldehyde, ethylene, ethyl acetate, nitroethane, acetic anhydride.
|
|
Ethylene
|
Ethanol, ethylene oxide, glycol, vinyl chloride, glyoxal, polyethene, styrene, butadiene, acetic acid.
|
|
Propane
|
Propanol, propionic acid, isopropyl ether, acetone, nitromethane, nitroethane, nitropropane.
|
|
Propylene
|
Glycerol, isopropyl alcohol, allyl alcohol, acrolein, nitroglycerine, dodecylbenzene, cumene, bakelite.
|
|
Hexane
|
Benzene, DDT, gammexane.
|
|
Heptane
|
Toluene
|
|
Cycloalkanes
|
Benzene, toluene, xylenes, adipic acid.
|
|
Benzene
|
Ethyl benzene, styrene, phenol, BHC (insecticide), adipic acid, nylon, cyclohexane, ABS detergents.
|
|
Toluene
|
Benzoic acid, saccharin, chloramine-T, benzyl chloride, TNT benzaldehyde, benzal chloride.
|
Email based Chemistry assignment help - homework help at Expertsmind
Are you searching chemistry expert for help with Characteristics of Hydrocarbons questions? Characteristics of Hydrocarbons topic is not easier to learn without external help? We at www.expertsmind.com offer finest service of Chemistry assignment help and chemistry homework help. Live tutors are available for 24x7 hours helping students in their Characteristics of Hydrocarbons related problems. We provide step by step Characteristics of Hydrocarbons question's answers with 100% plagiarism free content. We prepare quality content and notes for Characteristics of Hydrocarbons topic under chemistry theory and study material. These are avail for subscribed users and they can get advantages anytime.
Why Expertsmind for assignment help
- Higher degree holder and experienced experts network
- Punctuality and responsibility of work
- Quality solution with 100% plagiarism free answers
- Time on Delivery
- Privacy of information and details
- Excellence in solving chemistry queries in excels and word format.
- Best tutoring assistance 24x7 hours