Cathode rays, discovered by Sir Willium Crooke are the stream of electrons. They may be provided by using a discharge tube containing gas at a low pressure of the order of 10-2 mm of Hg. At that pressure the gas particles ionize and the emitted electrons travel towards positive potential of anode. The positive ions touch the cathode to produce emission of electrons from cathode. These electrons also go towards anode. Thus the cathode waves in the discharge tube are the electrons given due to ionization of gas and that emitted by cathode due to collision of positive ions.
Properties of cathode rays
(i) Cathode waves travel in straight path.
(ii) Cathode rays exert mechanical force on the objects they strike.
(iii) Cathode rays produce fluorescence.
(iv) When cathode rays strike a solid body, specially a metal of higher atomic weight and high melting point X-rays are emitted from the objects.
(v) Cathode rays ionize the gases through which they are passed.
(vi) Cathode rays can penetrate through thin foils of metal.
(vii) Cathode rays are found to have velocity ranging 1/30 to 1/10 of velocity of light.
J.J. Thomson's method to determine specific charge of electron
|
It's working is based on the fact that if a beam of electron is subjected to the crossed electric field and magnetic field , it experiences a force due to each field. In case the forces on the electrons in the electron beam due to these fields are equal and reverse, the beam acts undeflected.
|
|
C = Cathode, A = Anode, F = Filament, LT = Battery to heat the filament, V = potential difference to accelerate the electrons, SS' = ZnS coated screen, XY = metallic plates (Electric field produced between them)
(i) When no field is applied, the electron beam produces illuminations at point P.
(ii) In the presence of any field (electric and magnetic) electron beam deflected up or down (illumination at or )
(iii) If both the fields are applied simultaneously and adjusted such that electron beam passes undeflected and produces illumination at point P.
In this type; Electric force = Magnetic force => eE = evB => v = E/B; velocity of electron
As electron beam accelerated from cathode to anode its potential energy at the cathode appears as increase in the K.E. at the anode. If suppose V is the potential difference between cathode and anode then, potential energy = eV
And gain in kinetic energy at anode will be K.E. = 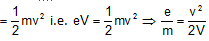
=> 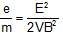
Thomson found, 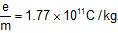
Email based Physics assignment help - homework help at Expertsmind
Are you searching physics expert for help with Cathode rays questions? Cathode rays topic is not easier to learn without external help? We at www.expertsmind.com offer finest service of Physics assignment help and physics homework help. Live tutors are available for 24x7 hours helping students in their Cathode rays related problems. We provide step by step Cathode rays question's answers with 100% plagiarism free content. We prepare quality content and notes for Cathode rays topic under physics theory and study material. These are avail for subscribed users and they can get advantages anytime.
Why Expertsmind for assignment help
- Higher degree holder and experienced experts network
- Punctuality and responsibility of work
- Quality solution with 100% plagiarism free answers
- Time on Delivery
- Privacy of information and details
- Excellence in solving physics queries in excels and word format.
- Best tutoring assistance 24x7 hours