The acceleration due to gravitational force on the surface of earth can be determined by using a simple pendulum.
Principle: For small angular deflections (upto 15°), the time period of a simple pendulum is given by
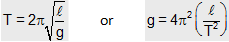
The above equation suggests that the value of gravity 'g' can be obtained by determining the average value of 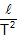 . Experimentally, for different values of length l the time period T is measured and graph is plotted between l and T2. The slope of the graph gives the average value of
. Experimentally, for different values of length l the time period T is measured and graph is plotted between l and T2. The slope of the graph gives the average value of 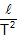 , which on multiplying with gives the value of g.
, which on multiplying with gives the value of g.
Procedure:
(i) The radius of the bob is obtained by vernier callipers.
(ii) A cotton thread of length about 150 cm is taken. Its one end is connected with the bob and the other end is passed through two half pieces of a cork, which is held firmly in the clamp stand.
(iii) Ink marks are made at distances 140 cm, 130 cm, 100 cm, 90 cm from the top of the bob.
Note that: the length of the hook is included in the measured length.
(iv) The stand is placed on the table such that the bob is 2 cm above the floor. With a piece of chalk two mutually perpendicular lines are drawn on the floor: one line AB parallel to the table and the other line CD perpendicular to table. The position of the stand is adjusted so that the bob lies exactly above the intersection O of two lines when at rest and moves parallel to the line AB when oscillates.
(v) Two markings E and F are made symmetrically about O at a distance about 3 to 4 cm. It defines the amplitude of oscillation about O. The bob is slowly displaced from O to E or F and then left. The bob oscillates about the point O along the line AB.
Note that
• the bob does not spin about its own axis while moving.
• the bob does not move in a horizontal circle.
|
(vi) When the bob reaches O for the first time, the stop watch is started and the time period for 2O complete oscillations is counted. One again the time period for 2O oscillations is counted and the average of the two observations is recorded.
|
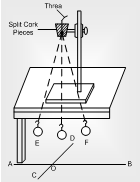
Figure Measurement of acceleration due
to gravity by using simple pendulum
|
(vii) The same observations are repeated by successively decreasing the length of the string by 10 cm. In this way, five observations are taken at different length
Email based Physics assignment help - homework help at Expertsmind
Are you searching physics expert for help with Calculating G using simple pendulum questions? Calculating G using simple pendulum topic is not easier to learn without external help? We at www.expertsmind.com offer finest service of Physics assignment help and physics homework help. Live tutors are available for 24x7 hours helping students in their Calculating G using simple pendulum related problems. We provide step by step Calculating G using simple pendulum question's answers with 100% plagiarism free content. We prepare quality content and notes for Calculating G using simple pendulum topic under physics theory and study material. These are avail for subscribed users and they can get advantages anytime.
Why Expertsmind for assignment help
- Higher degree holder and experienced experts network
- Punctuality and responsibility of work
- Quality solution with 100% plagiarism free answers
- Time on Delivery
- Privacy of information and details
- Excellence in solving physics queries in excels and word format.
- Best tutoring assistance 24x7 hours