Application of Le-Chatelier's principle
The Le-Chateliers principle has a great significance for the chemical, physical systems and in day to day life in a state of equilibrium.
(1) The applications to chemical equilibrium
(i) Synthesis of ammonia (Haber's process)
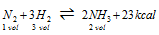 (exothermic)
(exothermic)
(a) High pressure ( Δn <0)
(b) Low temperature
(c) Excess of N2 and H2
(d) Removal of NH3 favours forward reaction.
(ii) Formation of sulphur trioxide
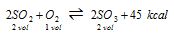 (exothermic)
(exothermic)
(a) High pressure ( Δn<0)
(b) Low temperature
(c) Excess of SO2 and O2, favours the reaction in forward direction.
(iii) Synthesis of nitric oxide
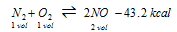 (endothermic )
(endothermic )
(a) High temperature
(b) Excess of N2 and O2
(c) Since reaction takes place without change in volume i.e., Δn=0, pressure has no effect on equilibrium.
(iv) Formation of nitrogen dioxide
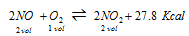
(a) High pressure
(b)Low temperature
(c) Excess of NO and O2 favors the reaction in forward direction.
(v) Dissociation of the phosphorus pentachloride
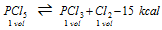
(a) The low pressure or high volume of container, Δn>0
(b) High temperature
(c) Excess of PCl5
(2) The applications to physical equilibrium
(i) Melting of the ice (Ice - water system)
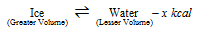
(In this reaction volume is decreased from the 1.09 cc to 1.01 cc per gm.)
(a) At the high temperature more water is formed as it absorbs the heat.
(b) At the high pressure more water is formed as it is accompanied by the decrease in volume.
(c) At the higher pressure, melting point of the ice is lowered, while the boiling point of water is increased.
(ii) Melting of sulphur : 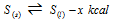
(This reaction accompanies increase in volume.)
(a) At the high temperature, more liquid sulphur is formed.
(b) At the higher pressure, less sulphur will melt as melting increases the volume.
(c) At the higher pressure, melting point of sulphur gets increased.
(iii) The boiling of water (water- water vapour system)
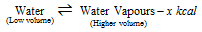
(It is accompanied by the absorption of heat and increase in volume.)
(a) At the high temperature more vapours are formed.
(b) At the higher pressure, vapours will be converted into the liquid as it decreases volume.
(c) At the higher pressure, boiling point of water is increased (it is principle of the pressure cooker).
(iv) Solubility of salts: If solubility of a salt is accompanied by the absorption process of the heat, solubility of it increases with the rise in temperature; for example NH4Cl, K2SO4, KNO3 etc.
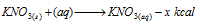
On the other hand if it is accompanied by evolution of heat, solubility decreases with increase in temperature; for example CaCl2, Ca(OH)2, NaOH, KOH etc.
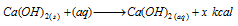
The relation which we can found between the vapour density and the Degree of dissociation
In the below reversible chemical equation.
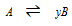
Initial mol 1 0
At equilibrium (1-x) yx x = degree of dissociation
Number of moles of A and B at equilibrium = 1-x+yx = 1+x(y-1)
If initial volume of 1 mole of A is V, then volume of equilibrium mixture of A and B is, = [1+x(y-1)]V
Molar density before dissociation,
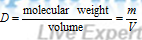
Molar density after dissociation process ; 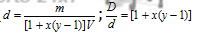 ;
;
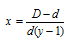
y is the number of moles of products from one mole of reactant. D/d is also called Van't Hoff factor.
In terms of molecular mass, 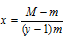
Where M = Initial molecular mass,
m = molecular mass at equilibrium
Thus for the equilibria
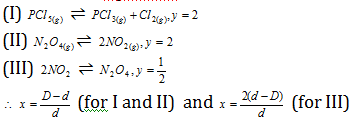
Also D * 2= Molecular weight (theoretical value)
D * 2 = Molecular weight (abnormal value) of the mixture.
Email based Chemistry assignment help - homework help at Expertsmind
Are you searching chemistry expert for help with Application of Le-Chatelier's principle questions? Application of Le-Chatelier's principle topic is not easier to learn without external help? We at www.expertsmind.com offer finest service of Chemistry assignment help and chemistry homework help. Live tutors are available for 24x7 hours helping students in their Application of Le-Chatelier's principle related problems. We provide step by step Application of Le-Chatelier's principle question's answers with 100% plagiarism free content. We prepare quality content and notes for Application of Le-Chatelier's principle topic under chemistry theory and study material. These are avail for subscribed users and they can get advantages anytime.
Why Expertsmind for assignment help
- Higher degree holder and experienced experts network
- Punctuality and responsibility of work
- Quality solution with 100% plagiarism free answers
- Time on Delivery
- Privacy of information and details
- Excellence in solving chemistry queries in excels and word format.
- Best tutoring assistance 24x7 hours