The application of Electrochemical series
(i) Reactivity of the metals: The activity of the metal depends on its tendency to lose electron or electrons, i.e., tendency to form cation . This tendency depends on the magnitude of standard reduction potential. The metal which posses high negative value (or smaller positive value) of standard reduction potential readily loses the electron or electrons and is converted into cation. Such type of metal is said to be chemically active. Chemical reactivity of the metals decreases from top to bottom in the series. The metals which are higher in the series is more active than the metal lower in the series. The examples are given as follows,
(a) Alkali metals and alkaline earth metals having high negative values of standard reduction potentials are chemically active. These react with the cold water and evolve hydrogen. These willingly dissolve in acids forming
consequent salts and combine with those substances which accept electrons.
(b) Metals such as Pb, Co, Sn, Fe, Ni, etc., which lie a little down in series do not react with cold water but react with steam to evolve the hydrogen.
(c) Metals such as Ag Cu, and Au which lie below the hydrogen are less reactive and do not evolve hydrogen from water.
(ii) Electropositive character of metals : The electropositive character also depends on the tendency to lose electron or electrons. Such as reactivity, the electropositive character of metals decreases from top to bottom in electrochemical series. On basis of the standard reduction potential values, metals are separated into the three groups
(a) Strongly electropositive metals: Metals having standard reduction potential near about - 2.0 volt or more negative such as alkaline earth metals alkali metals are strongly electropositive in the nature.
(b) Moderately electropositive metals : The metals possessing values of reduction potentials between 0.0 and nearly about - 2.0 volt are moderately electropositive Ni, Zn, Fe, Al, Co, etc., belong to this group.
(c) Weakly electropositive: The metals which are below hydrogen and possess positive values of reduction potentials are weakly electropositive metals. Ag, Hg, Cu, etc., belong to this group.
(iii) Displacement reactions
(a) To predict whether a given metal will displace the other, from its salt solution: A metal higher in the series will displace the metal from its solution which is lower in the series, that is The metal having low standard reduction potential will displace the metal from its salt's solution which has higher value of standard reduction potential. The metal higher in series has greater tendency to provide electrons to the cations of the metal to be precipitated.
(b) Displacement of one nonmetal from its salt solution by another nonmetal: A non-metal higher in the series (towards bottom side), that is having high value of reduction potential will displace another non-metal with lower reduction potential, that is occupying place above in series. Non-metal's which possess the high positive reduction potentials have the tendency to accept the electrons readily. These electrons are given by the ions of the nonmetal having low value of reduction potential. Hence, Cl2 can displace bromine and iodine from the iodides and bromides.
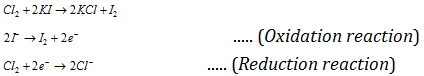
[The activity or electronegative character or oxidising nature of the nonmetal increases as the value of reduction potential increases.]
(c) Displacement of the hydrogen from dilute acids by the metals : The metal which can give electrons to H- ions present in dilute acids for reduction, evolve hydrogen from dilute acids.
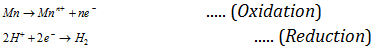
The metal possessing negative values of the reduction potential possess property of losing electron or electrons.
Therefore, the metals occupying top positions in electrochemical series readily liberate hydrogen from dilute acids and on descending in the series tendency to liberate the hydrogen gas from dilute acids decreases.
The metals which are under hydrogen in the electrochemical series such as Cu, Hg, Au, Pt, and more do not evolve hydrogen from the dilute acids.
(d) Displacement of hydrogen from water: Iron and the metals above iron are capable of liberating hydrogen from water. Its tendency decreases from top to the bottom in electrochemical series. The alkali and alkaline earth metals liberate hydrogen from the cold water but Zn, Mg and Fe liberate hydrogen from the hot water or steam.
(iv) Reducing power of metals: Reducing nature depends on the tendency of losing electron or electrons. The more the negative reduction potential, the more will be the tendency to lose electron or electrons. Therefore reducing nature decreases from top to the bottom in electrochemical series. The power of reducing agent increases, as standard reduction potential becomes more and more negative. The Sodium is a stronger reducing agent than the zinc and zinc is the stronger reducing agent than iron. (Decreasing order of the reducing nature)
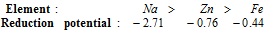
The alkaline earth metals and alkali are strong reducing agents.
(v) Oxidising nature of non-metals : Oxidising nature depends on the tendency to accept electron or electrons. More the value of reduction potential, higher is the tendency to accept electron or electrons. Thus, oxidising nature increases from top to bottom in the electrochemical series. The strength of an oxidising agent increases as the value of reduction potential becomes more and more positive.
F2 (Fluorine) is a stronger oxidant than Cl2, Br2 and I2, Cl2 (Chlorine) is a stronger oxidant than Br2 and I2
Thus, in electrochemical series
(vi) Thermal stability of metallic oxides : The thermal stability of metal oxide depends on its electropositive nature. Since the electropositivity decreases from top to the bottom, the thermal stability of the oxide also decreases from top to the bottom. The oxides of metals having high positive reduction potentials are not stable towards heat. Metals which are placed under copper in the periodic table form unstable oxides, which mean these are decomposed on heating.
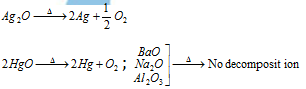
(vii) Extraction of metals: A more electropositive metal can displace a less electropositive metal from its salt's solution. This is the principle which is applied for the extraction of the Ag and Au by cyanide process. Silver from solution containing the sodium argento cyanide, NaAg(CN)2, can be obtained by addition of the zinc as it is more electro-positive than Ag
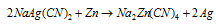
Email based Chemistry assignment help - homework help at Expertsmind
Are you searching chemistry expert for help with Application of Electrochemical series questions? Application of Electrochemical series topic is not easier to learn without external help? We at www.expertsmind.com offer finest service of Chemistry assignment help and chemistry homework help. Live tutors are available for 24x7 hours helping students in their Application of Electrochemical series related problems. We provide step by step Application of Electrochemical series question's answers with 100% plagiarism free content. We prepare quality content and notes for Application of Electrochemical series topic under chemistry theory and study material. These are avail for subscribed users and they can get advantages anytime.
Why Expertsmind for assignment help
- Higher degree holder and experienced experts network
- Punctuality and responsibility of work
- Quality solution with 100% plagiarism free answers
- Time on Delivery
- Privacy of information and details
- Excellence in solving chemistry queries in excels and word format.
- Best tutoring assistance 24x7 hours