(1) Amplitude (a) : Maximum displacement of a vibrating particle of medium from it's mean position is called amplitude.
|
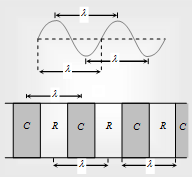
(2) Wavelength (l) : (i) It is the length of one wave.
(ii) Wavelength is same to the distance covered by the wave during the time in which any one particle of the medium completes one vibration about its mean position.
(iii) Wavelength is the displacement between any two nearest particles of the medium, vibrating in the same phase.
(iv) Distance covered by the wave in one time period is known as wavelength.
(v) In transverse wave motion:
λ = Displacement between the centers of two consecutive crests.
λ = Displacement between the centers of two consecutive troughs.
λ = Displacement in which one trough and one crest are contained.
|
|
(vi) In longitudinal wave motion:
λ = Displacement between the centers of two consecutive compressions.
λ = Displacement between the centers of two consecutive rarefactions.
λ = Displacement in which one compression and one rarefaction contained.
(3) Frequency: (i) Value of vibration of a particle is defined as the number of vibrations completed by particle in one second.
(ii) It is the value of complete wavelengths traversed by the wave in one second.
(iii) Value of frequency are hertz (Hz) and per second.
(4) Time period: (i) Time section of vibration of particle is defined as the time taken by the particle to complete one vibration about its mean position.
(ii) It is the time given by the ray to travel a distance equal to one wavelength.
(5) Relation between frequency and time period:
Time period = 1/Frequency => T = 1/n
(6) Relation between velocity, frequency and wavelength: v = nλ
Speed (v) of the ray in a given medium depends on the elastic and inertial property of the medium.
Frequency (n) is characterized by the source which gives disturbance. Different sources may give vibration of different frequencies. Wavelength (λ) will differ to keep nλ = v = constant
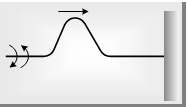
(7) Wave pulse : It is a short wave produce in a medium when the disturbance created for a short time.
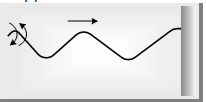
(8) Wave train : A series of ray pulse is known as wave train.
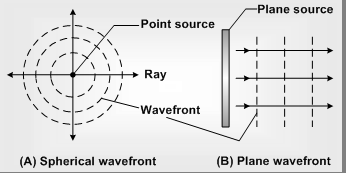
(9) Wave front : A wave front is a line or surface on which the disturbance has the same phase at each position. If the source is periodic, it produces a succession of ray front, each of the similar shape. Ripples on a pond are the example of wave fronts.
(10) Wave function: It is a mathematical description of the disturbance prepared by a ray. For a string, the wave function is a distance for sound rays. It is a density or pressure fluctuation where as for light waves it is electric or magnetic field.
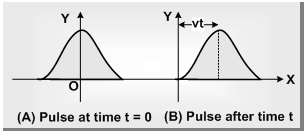
Now let us consider a one dimensional wave traveling with reference to x-axis. During ray motion, a particle with equilibrium position x is displaced some distance y in the direction perpendicular to the x-axis. In that part y is a function of position (x) and time (t).
i.e. y ¾ f(x, t). This is called wave function.
Let the wave pulse is traveling with a speed v, after a time t, the pulse reaches a distance vt along the +x-axis as given. The ray function now can represented as y = f(x-vt)
|
If the wave pulse is traveling along -x-axis then y = f(x-vt) quantities, x, v, t must appear in combinations x+vt or x-vt .
Thus y = (x-vt)2, √(x-vt), Ae-B(x-vt)2 etc. represents traveling waves while y = (x2-v2t2), √x- √vt ,Asin(4x2-9t2) etc. doesn't represents a wave.
|
|
(11) Harmonic Wave : If a traveling wave is a sin or cos function of (x ± vt) the wave is said to be harmonic or plane progressive wave.
(12) The wave equation : All the traveling waves satisfy a differential equation which is called the wave equation. It is given by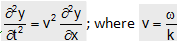
It is compared by any relation of the form y = f(x±vt)
(13) Angular wave number or propagation constant (k) : Number of wavelengths in the distance 2p is called the propagation constant or wave number i.e.k = 2∏/λ.
It is unit is rad/m.
(14) Wave velocity (v) : It is the distance traveled by the disturbance in one time period. It only relays on the properties of the medium and it independent of time and position.
v = nλ = λ/T = ω/2∏ = ω/k
(15) Group velocity (vg) : The velocity with which the group of waves travels is known as group velocity
or the velocity with which a ray packet goes is known as group velocity vg = dω/dk
(16) Phase (f) : The quantity which express at any instant, the displacement of the particle and it's direction of motion is called the phase of the particle.
|
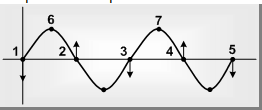
If two particles of the medium, at any instant are at the same distance in the same direction from their equilibrium positions and are moving in the same direction then they are said to be in similar medium e.g. In the following diagram particles 1, 3 and 5 are in same medium and position 6, 7 are also in similar medium.
|
|
(17) Intensity of wave : The wave intensity is defined as the average amount of energy flow in medium per unit time and per unit of its cross-sectional area. It's value measured by W/m2
Hence intensity 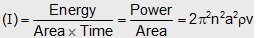
(when v, ρ = constant)
where a = Amplitude n = Frequency, v = Wave velocity, ρ ¾ Density of medium.
At a displacement r from a position source of power P the intensity is given by 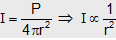
|
The human ear can hear sound of intensity up to . This is called threshold of intensity. The maximum limit of intensity of sound which can be tolerated by human ear is . This is called threshold of pain.
|
|
(18) Energy density : The energy associated with unit volume of the medium is defined as energy density.
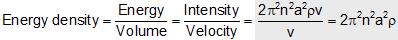
Email based Physics assignment help - homework help at Expertsmind
Are you searching physics expert for help with Amplitude wavelength and frequency of waves questions? Amplitude wavelength and frequency of waves topic is not easier to learn without external help? We at www.expertsmind.com offer finest service of Physics assignment help and physics homework help. Live tutors are available for 24x7 hours helping students in their Amplitude wavelength and frequency of waves related problems. We provide step by step Amplitude wavelength and frequency of waves question's answers with 100% plagiarism free content. We prepare quality content and notes for Amplitude wavelength and frequency of waves topic under physics theory and study material. These are avail for subscribed users and they can get advantages anytime.
Why Expertsmind for assignment help
- Higher degree holder and experienced experts network
- Punctuality and responsibility of work
- Quality solution with 100% plagiarism free answers
- Time on Delivery
- Privacy of information and details
- Excellence in solving physics queries in excels and word format.
- Best tutoring assistance 24x7 hours