Adjusting Business Decisions for Risk
Diminishing marginal utility of money leads to risk aversion that is reflected in the capitalization rate applied by investors in determining the value of future return. Risk adjusted discount rate is commonly used to determine the present value of the future profits associated with an investment. Given the streams of future profits pt the basic evaluation framework
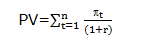
is modified by using an appropriate risk adjusted interest or discount rate for r. Most investors are wiling to accept greater risk only if there is a promise of greater returns compared to an investment with less risk. For example, the return on an insured bank certificate of deposit is 10 per cent per year. No rational investor will invest in very risky ventures such as oil drilling or gold mining unless the expected return is considerably higher than 10 per cent per year.
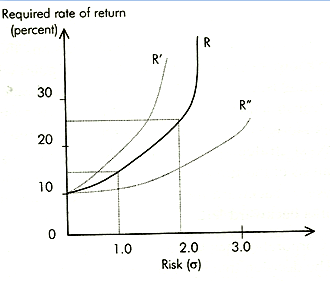
The risk adjusted discount rate reflects the manager's trade-off between risk and return as shown in Figure. Risk return trade-off function (curve R) shows all combinations of risk and return for which an investor is indifferent. The shape of the curve varies with the attitude of investors.
- A very risk averse person might have a trade-off function similar to dashed line R' - any increase in risk must carry with it a significant increase in return.
- A risk seeker may have a trade-off function similar to R". Here only a small increase in the rate of return is required to compensate a rather large increase in risk.
Suppose the rate of return associated with risk less investment is 10 per cent. The standard deviation in this case will be zero. For the investor with trade-off function R, if the risk is say, σ = 1.0, a 15 per cent rate of return is required. The difference between this 15 per cent return and riskless rate is referred as risk premium. If σ = 2.0, the trade-off function R indicates that a 22 per cent return is required for this person. Thus the risk premium is 12 percentage points. In evaluating investments, these differential discount rates would be used to evaluate the present value of future profits. That is, net cash flows for a high-risk investment would be discounted using a higher discount rate than would be used for a low-risk alternative.
Managerial Economics Tutoring - Assignment Help
Our online managerial economics experts are here for your help. Expertsmind.com online assignment help-homework help brings you high grade in your courses and examination, We at Expertsmind.com offers managerial economics assignment help, managerial economics homework help and projects help. We offer complete package of managerial economics online tutoring for 24x7 hours.
ExpertsMind.com - Adjusting Business Decisions for Risk Assignment Help, Adjusting Business Decisions for Risk Homework Help, Adjusting Business Decisions for Risk Assignment Tutors, Adjusting Business Decisions for Risk Solutions, Adjusting Business Decisions for Risk Answers, Risk and Decision Making Assignment Tutors