Acid derivatives
The compounds which are obtained by replacing the -OH of the carboxylic group by other atoms or groups such as X-, NH2, - OR and 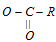 are known as acid derivatives.
are known as acid derivatives.
· 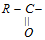 group is general to all the derivatives and is known as acyl group and these derivatives are termed as acyl compound.
group is general to all the derivatives and is known as acyl group and these derivatives are termed as acyl compound.
· The important derivatives are given below :
|
Group replacing - OH
|
Name
|
Structure
|
|
(x = F, Cl, Br, I)
|
Acyl halide
|
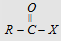
|
|
-NH2
|
Amide
|
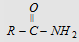
|
|
-OR'
|
ester
|
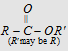
|
|
-OOCR
|
anhydride
|
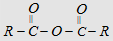
|
Reactivity
Acyl derivatives are characterised by nucleophilic substitution reactions.
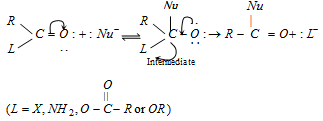
The relative reactivities of several acyl elements have been found to be in the following order:
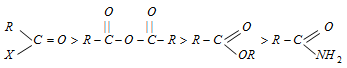
Out of acid halides, the acid chlorides are more important ones.
The overall order of reactivity can be accounted for in terms of the following three factors:
(i) Basicity of the leaving group (ii) Resonance effects and (iii) Inductive effects.
(i) Basicity of the leaving group : Weaker bases are good leaving groups. Hence, the acyl derivatives with weaker bases as leaving groups are more reactive. Chloride ion is the weakest base while - NH2 is the strongest base. Thus, acyl chlorides are most reactive and amides are least reactive.
(ii) Resonance effect : The leaving group in each case has an atom with lone pair of electrons adjacent to the carbonyl group. The compound exists, therefore, as a resonance hybrid.
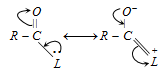
This makes the molecule more stable. The greater the stabilization, the smaller is the reactivity of the acyl compound.
However, acyl chlorides are least affected by resonance. Due to lower stabilization, the acid chlorides are more reactive as the loss of -Cl is easier. Greater stabilization is achieved by resonance in esters and amides and thus, they are less reactive.
(iii) Inductive effect : Higher the -I effect, more reactive is the acyl compound. Inductive effect of oxygen in ester is greater than nitrogen in amide, hence ester is more reactive than an amide.
Email based Chemistry assignment help - homework help at Expertsmind
Are you searching chemistry expert for help with Acid derivatives questions? Acid derivatives topic is not easier to learn without external help? We at www.expertsmind.com offer finest service of Chemistry assignment help and chemistry homework help. Live tutors are available for 24x7 hours helping students in their Acid derivatives related problems. We provide step by step Acid derivatives question's answers with 100% plagiarism free content. We prepare quality content and notes for Acid derivatives topic under chemistry theory and study material. These are avail for subscribed users and they can get advantages anytime.
Why Expertsmind for assignment help
- Higher degree holder and experienced experts network
- Punctuality and responsibility of work
- Quality solution with 100% plagiarism free answers
- Time on Delivery
- Privacy of information and details
- Excellence in solving chemistry queries in excels and word format.
- Best tutoring assistance 24x7 hours