Generally accepted accounting principles (gaap), conventions and concepts
The primary objective of the Financial Accounting is to communicate and provide information to the investors and creditors on the economic activities of the enterprise that will help them in their investment decisions. The financial statements of different entities must be prepared on a uniform basis, and an enterprise must maintain consistency in preparing the financial statements. Therefore, the language of accounting needs to adhere to a framework of principles, known as Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP). Accounting principles may be defined as rules of action and conduct that are adopted by accountants while recording the accounting transactions. Unlike the principles of Physics, Chemistry and other Natural sciences (that can be verified by observation), accounting principles have been evolved and established by humans. These principles enable to a certain extent standardization in recording and reporting of information.
Statement No. 4 of the Accounting Principles Board (US) on 'Basic concepts and Accounting principles Underlying Financial Statements of Business Enterprises' describes accounting principles as follows:
"Generally Accepted Accounting Principles incorporate the consensus at a particular time as to which economic resources and obligations should be recorded as assets and liabilities by financial accounting, which changes in assets and liabilities should be recorded, when these changes are to be recorded, how the assets and liabilities and changes in them should be measured, what information should be disclosed and which financial statements should be prepared."
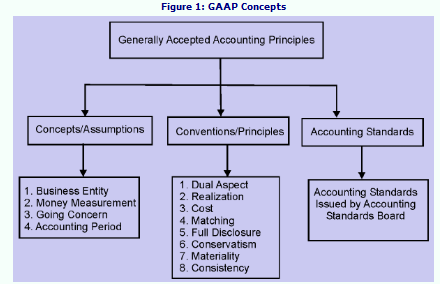
Accounting principles are the rules, bases, conventions and procedures adopted by management in preparing accounting records and presenting financial statements. These principles, assumptions or rules have been developed over a number of years. These principles can be categorized into three categories viz., (i) Accounting Concepts/Assumptions, (ii) Accounting Conventions, and (iii) Accounting Standards. Accounting concepts are based on logical considerations and help in recording the business transactions. Accounting conventions are based on what is practicable and include those customs and traditions, which guide the accountant in the preparation of financial statements. Accounting Standards are the guidelines issued by Accounting Standards Board of a country for financial reporting. Generally, these standards are issued to bring uniformity in financial reporting in a particular country. For multinational operating countries, there are International Accounting Standards for financial reporting.