Molecular speeds or velocities
(1) At any specific time, in the given sample of gas all the molecules do not have same speed, because of the frequent molecular collisions with the walls of the container and also with each other, the molecules move with ever changing speeds and also with the ever changing direction of motion.
(2) In accordance to Maxwell, at the specific temperature the distribution of speeds remains constant and this distribution is referred to as Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution and given by the expression given below,
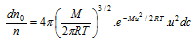
where, dno = Number of molecules out of total number of molecules n, having velocities between c and c+dc, dno/n = Fraction of the total number of molecules, M = molecular weight, T = absolute temperature. The exponential factor 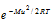 is called Boltzmann factor.
is called Boltzmann factor.
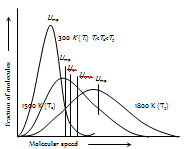
(3) Maxwell gave distribution curves of molecular speeds for CO2 at different temperatures. Special features of the curve are defined as follows :
(i) The fraction of molecules with the two high or two low speeds is quite small.
(ii) No molecules have zero velocity.
(iii) At first the fraction of the molecules increases in velocity till the peak of the curve which pertains to most probable velocity and thereafter it falls with increase in velocity.
(4) Types of molecular speeds or Velocities can be described as follows
(i) The root mean square velocity (urms) : It is square root of the mean of the squares of the velocity of a large number of the molecules of same gas.
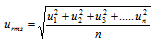
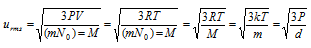
here k = Boltzmann constant = R/No
(a) For the same gas at the two different temperatures, the ratio of RMS velocities will be given as, 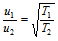
(b) For two different gases at the same temperature, the ratio of RMS velocities will be given as, 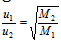
(c) RMS velocity at any temperature t degree C may be related to its value at Standard Temperature Pressure is given as, 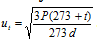 .
.
(ii) Average velocity : It is the average of various velocities possessed by the molecules.
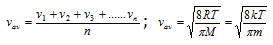
(iii) Most probable velocity : It is the velocity possessed by maximum number of molecules of a gas at a given temperature.
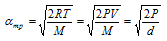
(5) Relation between molecular speeds or velocities,
(i) Relation between urms and vav: vav = 0.9213 * urms
or urms = 1.085 * vav
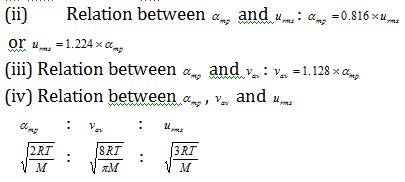
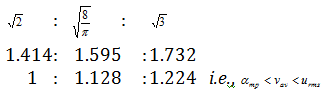
Email based Chemistry assignment help - homework help at Expertsmind
Are you searching chemistry expert for help with Molecular speeds or velocities questions? Molecular speeds or velocities topic is not easier to learn without external help? We at www.expertsmind.com offer finest service of Chemistry assignment help and chemistry homework help. Live tutors are available for 24x7 hours helping students in their Molecular speeds or velocities related problems. We provide step by step Molecular speeds or velocities question's answers with 100% plagiarism free content. We prepare quality content and notes for Molecular speeds or velocities topic under chemistry theory and study material. These are avail for subscribed users and they can get advantages anytime.
Why Expertsmind for assignment help
- Higher degree holder and experienced experts network
- Punctuality and responsibility of work
- Quality solution with 100% plagiarism free answers
- Time on Delivery
- Privacy of information and details
- Excellence in solving chemistry queries in excels and word format.
- Best tutoring assistance 24x7 hours