tRNA structure:
Transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules play an very important role in protein synthesis. Every tRNA becomes covalently bonded to a specific amino acid to create aminoacyl- transfer RNA that recognizes the corresponding codon in mRNA and ensures in which the correct amino acid is added to the growing polypeptide chain. The transfer RNAs are small molecules, only 74-95 nt long, that form distinctive cloverleaf secondary structures shown in the figure through internal base pairing. The stem-loops of the cloverleaf are called as arms:
- the anticodon arm holds in its loop the three nucleotides of the anticodon that will form base pairs with the complementary codon in mRNA in during translation;
- the DHU or D arm (with its D loop) contains dihydrouracil, and strange pyrimidine;
- the TΨC or T arm (with its T loop) holds another strange base, pseudouracil (indicate Ψ) in the sequence TΨC;
- Some transfer RNAs also have a variable arm (optional arm) that is 3-21 nt in size.
The other notable feature is the amino acid acceptor stem. That is where the amino acid becomes attached, at the 3 OH groups of the 3 -CCA sequence.
The three-dimensional structure of tRNA that was shown in the figure is even more complex because of additional interactions between the various units of secondary structure.
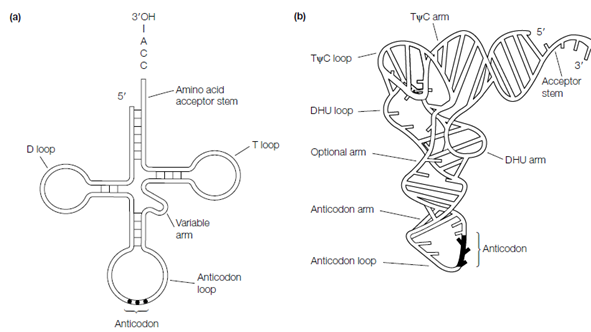
Figure: (a) Cloverleaf secondary structure of tRNA; (b) tertiary structure of tRNA (from Genetics: a Molecular Approach, second edition, T.A. Brown, Kluwer Academic Publishers, with permission).