Adiabatic Saturation:
The thermodynamic wet bulb temperature or adiabatic saturation temperature is the temperature on which the air might be brought to saturation state, adiabatically, from the evaporation of water in the flowing air.
The equipment utilized for the adiabatic saturation of air, in its easiest form, contain an insulated chamber having sufficient quantity of water. There is also an arrangement for additional water (known as make-up water) to flow into the chamber from its top, as illustrated in figure
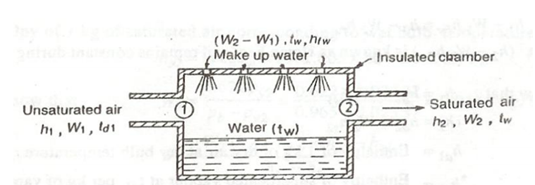
Adiabatic Saturation of Air
Consider the unsaturated air enters the chamber at section 1. Since the air flow through the chamber on a long sheet of water, the water evaporates that is carried with the passing stream of air, and the specific humidity of the air enhanced. The form water is added to the chamber at this temperature to do the water level constant. The air and water both are cooled up as the evaporation occur. This procedure continues till the energy transferred through the air to the water is equivalent to the energy needed to vaporise the water. While steady conditions are attained, the air passing on section two is saturated along water vapour. The temperature of the saturated air at section 2 is called as thermodynamic wet bulb temperature or adiabatic saturation temperature.
The adiabatic saturation procedure might be represented on T-s diagram as illustrated by the curve 1-2 in given figure
Throughout the adiabatic saturation procedure, the partial pressure of vapour enhanced, although the total pressure of the air-vapour mixture have constant. Initially the unsaturated air at dry bulb temperature td1 is cooled up adiabatically to dry bulb temperature td2 that is equivalent to the adiabatic saturation temperature tw. It can be noted down that the adiabatic saturation temperature is taken equivalent to the wet bulb temperature for all of practical reason.
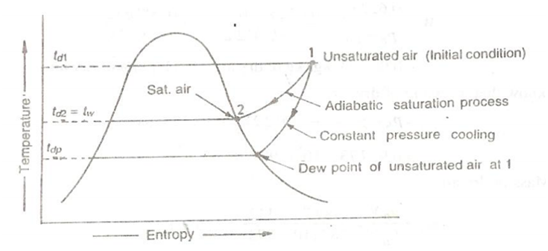
Figure: T-S Diagram for Adiabatic Saturation procedure
Assume h1 = Enthalpy of unsaturated air at section 1, W1= Specific humidity of air at section 1, h2, W2 = equivalent values of saturated air at section 2, and hfw= Sensible heat of water at adiabatic saturation temperature. To balancing the enthalpies of air at inlet & outlet (that means at sections 1 & 2),
h1 + (W2 - W1) hfw= h2 ...6.32
h1 - W1 hfw = h2 - W2 hfw ...6.33
The term (h2 - W2 hfw) is called as sigma heat & remains constant throughout the adiabatic process
We know that h1 = ha1 + W1hs1
h2 = ha2 + W2hs2
here
ha1 = Enthalpy of 1 kg of dry air at dry bulb temperature tdl,
hs1 = Enthalpy of superheated vapour at t per kg of vapour,
ha2 = Enthalpy of 1 kg of air at wet bulb temperature tw , and
hs2 = Enthalpy of saturated vapour at wet bulb temperature tw per kg of vapour.
Now the equation (6.33) may be written as following:
(ha1 + W1hs1) - W1 hfw = (ha2 + W2hs2) - W2hs2 ...6.34
W1(hs1 - hfw) = W2(hs2 - hfw) + ha2 - ha1 ...6.35
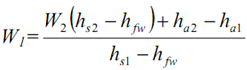 ...6.36
...6.36