Formation of the Carbon Dioxide Molecule:
While both shared electrons in a covalent bond come from the similar atom, the bond is known as a coordinate covalent bond. While both shared electrons come from the similar atom, a coordinate covalent bond is a single bond same in properties to a covalent bond. Below Figure described the bonds of the negatively-charged chlorate ion. An ion consists of one chlorine atom and three oxygen atoms along with a net charge of -1, and is created along with two coordinate covalent bonds and one covalent bond. A chlorine atom has efficiently gained an electron by the covalent bond that causes the in general negative charge.
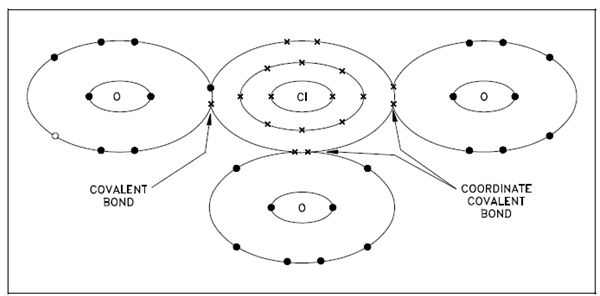
Figure: Coordinate Covalent Bond, Chlorate Ion ClO3
Covalent bonds could be either polar or nonpolar. While the shared pair of electrons is not shared regularly, one end of the bond is positive, and the other end is negative. That generates a bond along with two poles known as a polar covalent bond.
Molecules having polar covalent bonds are known as dipolar or polar molecules. Water is an instance of a polar molecule. While two atoms of the similar element share one or more pairs of electrons (such as H or N), every atom exerts the similar attraction for the shared electron pair or pairs. While the electron pairs are distributed or shared equally among the two such atoms, the bond is known as a nonpolar covalent bond. The molecule is called a nonpolar covalent molecule if all the bonds within a molecule are of this type.